Individuals with BSEP deficiency with one p.E297G or p.D482G mutation and one PPTM have a similarly severe disease course and low responsiveness to siEHC as those with two PPTMs.
Using a mouse model of BA and human liver gene expression data collected by ChiLDReN, we were able to confirm the likely activation of this pathway known as TWEAK/FN14 in association with liver fibrosis. We further showed that inhibition of this pathway pharmacologically was associated with near complete elimination of fibrosis in the mouse model of BA.
Large-scale proteomics identified SEMA6B, SFRP3, COMMD7, BMX, and VCAM1 as biomarkers highly associated with clinical portal hypertension in children with biliary atresia. The expression of the biomarkers in liver epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells support their potential role in the mechanisms that cause portal hypertension.
In a 1-year-old female patient with normal GGT cholestasis and bile duct paucity, we identified a homozygous truncating pathogenic variant (c.198delA, p.Gly67Alafs∗6) in the ABCC12 gene (NM_033226). Five additional rare ABCC12 variants, including a pathogenic one, were detected in our cohort.
Regional variation in glutathione metabolism underlies sensitivity to the biliary toxin biliatresone and may account for the reported association between BA transplant-free survival and glutathione metabolism gene expression.
Our finding of de novo variants in genes linked to evolutionarily conserved stress responses (STIP1 and REV1) suggests that exploration of how genetic susceptibility and environmental exposure may interact to cause BA is warranted.
In studies of liver tissues from infants with cholestasis, we identified a 14-gene expression pattern that associated with transplant-free survival for 2 years.
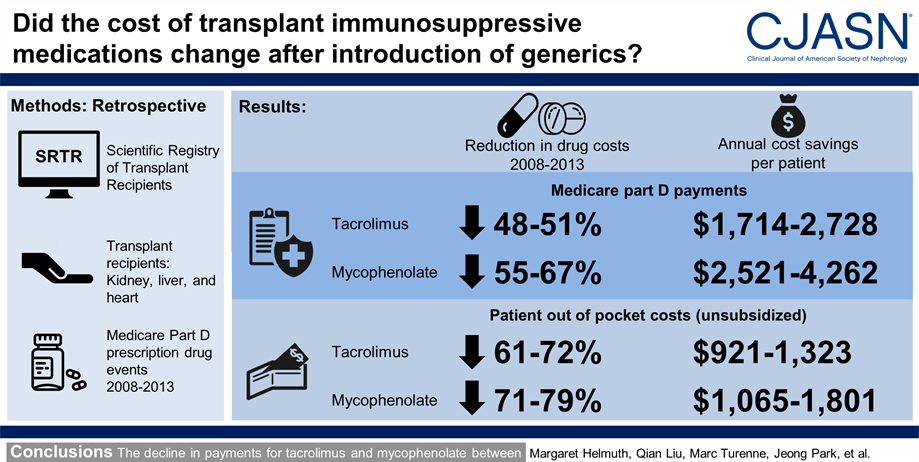
Generic medications reduce the lifetime costs of organ transplantation